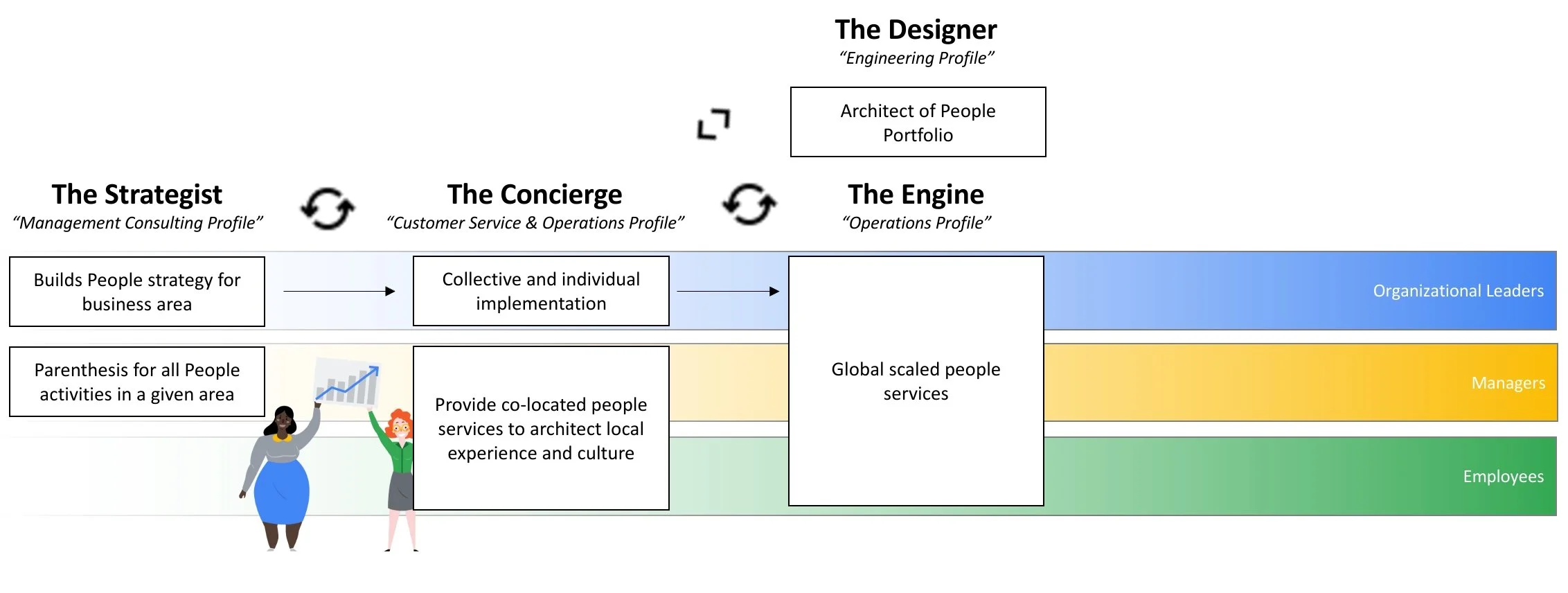
HR Operating Model
Every HR organization eventually reaches a point where it needs to define its operating model. The goal is to establish an efficient structure that delivers the desired business outcomes. This often involves a multi-faceted approach:
The Engine (Global Scaled People Services): Standard, high-volume tasks such as contract administration, mobility, payroll, and basic employee inquiries are best handled within a globally scaled people services model. This centralized approach ensures efficiency and consistency.
The Designer (Global Centers of Excellence): Functions like Total Rewards, Talent Development, and Compliance reside within global Centers of Excellence. These groups are responsible for developing policies, processes, and best practices, which are then adapted and implemented by the service model across the organization.
The Concierge (Local People Services): Not all operations can be globally scaled. Local requirements, such as dealing with unions or workers councils (common in European countries), and the need to create memorable people experiences necessitate a local presence. This "Concierge" model often includes location or event managers who act as the local face of HR, fostering local culture and driving employee engagement.
The Strategist (HR Business Partners): To drive organizational change and strategy, HR Business Partners develop the people strategy for their respective business areas. They then lead the end-to-end implementation of people-related initiatives, collaborating with all other HR functions.
A key component of the HR Organization model is the approach in which HR interacts with the organizations. This is a reflection of how HR leadership defines its role. More traditional HR organizations have a self-image creating policy and process and then executing it. In more advanced organizations the HR Organizations is a service and advisory function. I prefer a a model in which HR becomes a value driver for the organizations. In this model, HR does not see itself as a function supporting “the business” but understand itself as part of organizational success with responsibility to co-drive business outcomes.
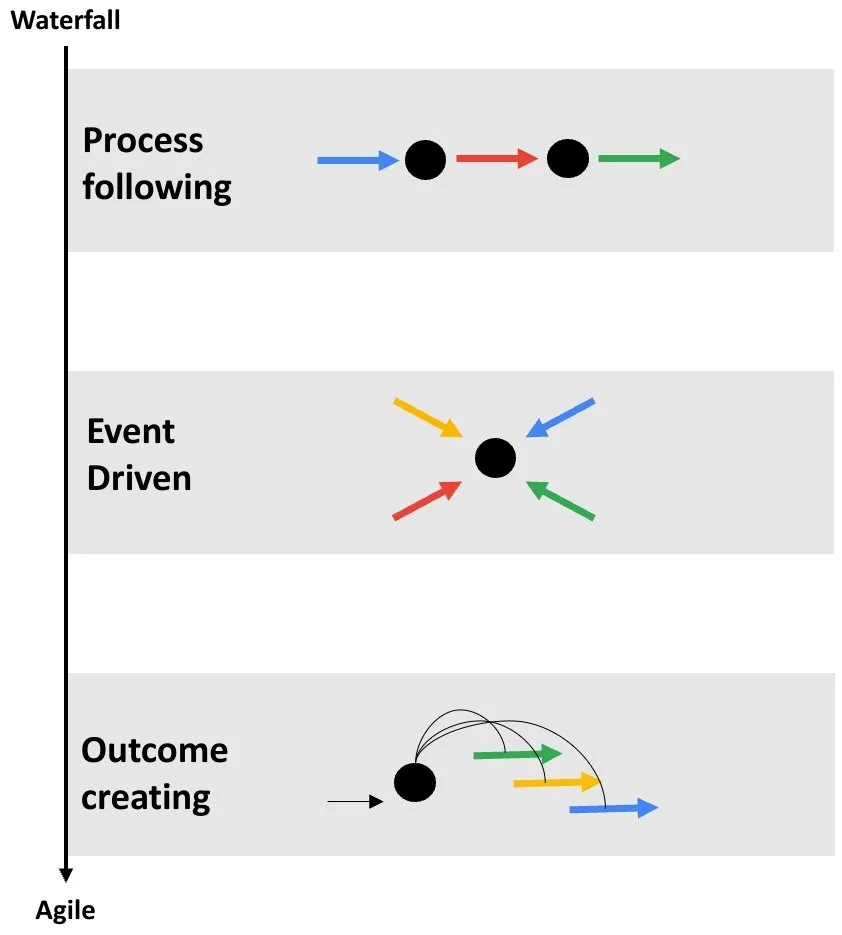
Process following
Classical HR model for processes in sync with the financial year of the company. Fiscal year is planned with specific milestones such as salary planning, talent review and performance rating.
Event Driven
Evolved approach in which HR tackles specific tasks or events that are non-standard or unscheduled. Flexibility to tackle events outside the regular process to successfully resolve the event. E.g. Off-cycle salary increases, restructurings, project implementations.
Outcome Creating
Co-accountable for business outcomes. Value creation by crafting people solutions for commercial impact of the organization. HR part of the business ecosystem to meet customer need. E.g. proactive performance management, organization growth and effectiveness.